What is Radon?
Radon is a gas that is located in the Periodic Table of Elements. Radon is labeled Rn. Radon cannot be seen, smelled, or tasted, but it may be a problem in your home.
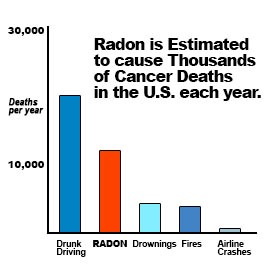
Radon is estimated to cause up to twenty-thousand deaths per year and that’s because when you breathe in air containing radon, you can get lung cancer. Radon has also been linked to bone cancer and has been able to damage the internal body structure as well.
Radon was a popular additive in products like toothpaste, hair creams and even food items in the early twentieth century, due to its supposed “healing” powers. Radon was subsequently removed when its carcinogenic properties were discovered years later by scientists. The Surgeon General has even warned that radon is the second leading cause of lung cancer today.
In the early 1990’s, The Environmental Protection Agency stated that Radon which can be located in the ground soil can seep into your water pipes and wells. A report to test for Radon in water was proposed and Eventually, an act was even set into an article in the Safe Water Drinking Act of 1996.
Where does Radon come from?
Radon comes from a breakdown of uranium and radium in soil, rock, and water. It can be found all over the United States and is able to get into any type of building and increase to enormous levels. Most people are likely to receive greater exposure to radon in their home. You can also note that Radon is one of the most heaviest gasses in our environment.
How does Radon get into your home?
Radon typically moves through the ground up to the air you breathe and into your home through cracks and other holes in the foundation. Your home traps radon inside, where it builds up in large amounts.
One out of every fifteen homes in the U.S. is estimated to have high radon levels. Radon can also be a huge problem in schools and workplaces as well.
What Radon test results Mean?
The average indoor radon level is estimated to be about 1.3 pCi/L, and about 0.4 pCi/L of radon is found outside in the air.
The United States Congress has set a long-term goal that indoor radon levels be no more than outdoor radon levels.
Most homes can be reduced to 2 pCi/L or lower. Even if your test result is below 4 pCi/L, you may want to test again in the future to be assured.
Radon gets to you through
- Cracks in solid floors
- Construction joints
- Cracks in walls
- Gaps in suspended floors
- Gaps around service pipes
- Cavities inside walls
- The water supply
Reducing Radon in your home?
Many methods can be used to reduce the amount of Radon that you have in your home. A method, such as sealing cracks in floors, walls, and under ceramic items may help to reduce radon. Sometimes, extra usage of piping and fans could help also.
Sub-slab depressurization removes radon gas below the concrete floor and foundation before it enters your home, it can also be used in crawl spaces. The methods that are used depends on the mitigation contractor you choose.

What's the risk?
Radon decays into particles that get trapped inside your lungs when you breath air. They break down further and eventually release small bursts of energy. These bursts can damage lung tissue and lead to lung cancer over the course of your lifetime, not everyone will obtain lung cancer. Smoking combined with radon is a serious health risk also, if you stop smoking and lower your radon level it can reduce your lung cancer risk greatly.




